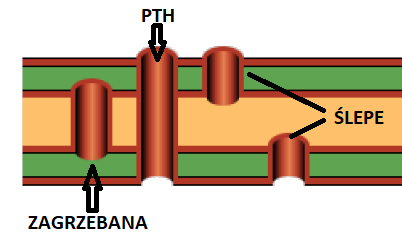
PCB elements: HOLES TYPES

Due a big variety of functions and applications of printed circuits the different types of the holes can be present in their structure. They can be classified in a general way – metalized / non-metalized or because of their shape or function etc.
The classification considering most types of holes types used in printed circuits is presented below.
Basic classification:
- vias/metalized holes
- standard – diameter from 0.2 mm
- micro-vias – diameter below 0.2 mm (typical: 0.1 mm; 0.15 mm)
- non-metalized holes: diameter from 0.25 mm
- without annular ring
- with the annular ring moved from the hole edge
- with the annular ring up to the hole edge.
Classification by what layers they pass through / what layers they connect:
- PTH/NPTH – they pass through the entire thickness of the PCB;
- blind/backdrilling – vias/holes drilled to the depth (visible from outside but only on one side of the PCB);
- buried vias – vias connecting the internal layers (not visible from outside).
Classification by a finishing method:
- not covered by a soldermask – without cover or covered with the protection layer e.g. HAL, ENIG etc.
- covered with a soldermask (usually not plugged)
- filled (copper, dielectric)
- filled and covered with a soldermask (standard)
- filled and covered with a soldermask (flat, bigger degree of filling).
Non-typical:
- slotholes:
- special case: slotholes 2D - the slothole length (L) is smaller or equal double it width (2D)
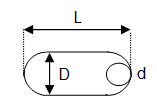 L ≤ 2*D sinkholes (beveled).
L ≤ 2*D sinkholes (beveled).
- sinkholes (beveled)
Classification by the diameter tolerance (examples):
- standard, typically: + 0.1 mm / - 0.05 mm
- pressfit: e.g. + 0.05 mm / - 0.05 mm.
The parameters and application of individual types of holes will be presented in the forthcoming articles.