Solder masks in printed circuits - types and basic functions

Mosaics of printed circuits are made from copper whose major advantage is excellent conductivity of electrical current and heat. At the same time, this metal is susceptible to the adverse effects of oxidation when in contact with air and moisture. In order to protect mosaics from environmental impact they are covered with a special paint called an anti-solder mask. Its name reveals another crucial role which it performs during the component assembling process — it protects the mosaics from the effect of the solder alloy, restricting it to the exposed, mask-free soldering areas. Other functions will be pointed further in the article as well as characteristic specifications, types and application.
Beside the applications mentioned above, the anti-solder masks also have some other important functions, including:
- the prevention of pad bridging via soldering (short circuit with tin).
- reduction in electrical breaks by adding an additional insulation barrier between the paths.
- reduction in solder consumption — thus restricting the total weight of the device and its cost.
- protection of the printed circuit against impurities and other environmental factors that have a negative impact on copper.
Protective masks can be divided into two types: permanent and temporary.
The former are most often applied on circuits in the form of liquid paint, which then is hardened by heat treatment or/and by ultraviolet radiation (photo 1). A less popular variant is a permanent dry mask. Unfortunately, it is more expensive and more difficult to apply, although it can be applied simultaneously on both sides of the laminate. The next part of the article mainly concerns wet masks due to the popularity of this technology.
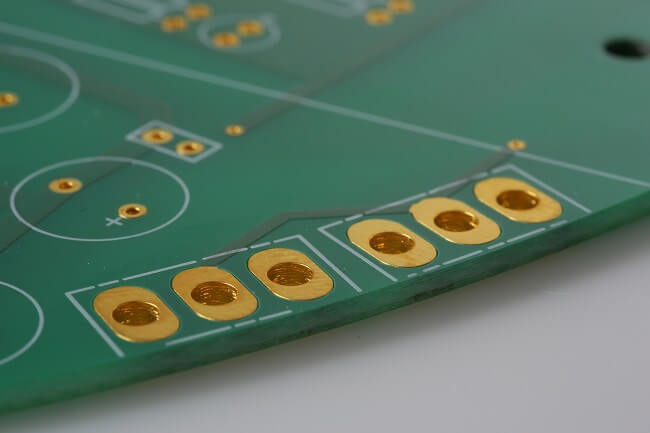
Photo. 1. Close up of a circuit with a standard semi-matte, green mask (curtain photomask, permanent).
Temporary masks are most often used for additional protection of certain groups of holes or connector strips before soldering during assembly.
This group of masks includes a so-called peelable mask which is applied by screen printing and with Kapton tape most often applied manually. These masks also prevent the holes being blocked with solder, allowing the through-hole elements to be embedded later. After assembly, they can be easily and safely removed from the circuits (photo 2.).
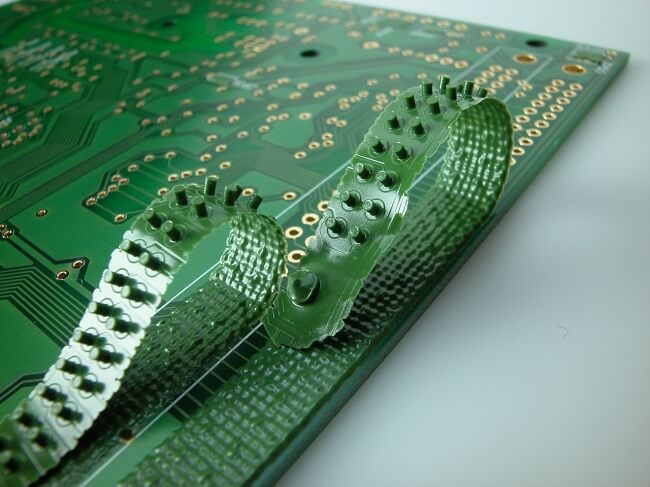
Photo 2. An example of a circuit with a peelable mask.
Check also: Solder masks in printed circuits - types and basic functions